Decreasing Chronic Absenteeism
In Chicago, 36 percent of students in Head Start programs miss more than 10 percent of school— more than a month of instructional time.
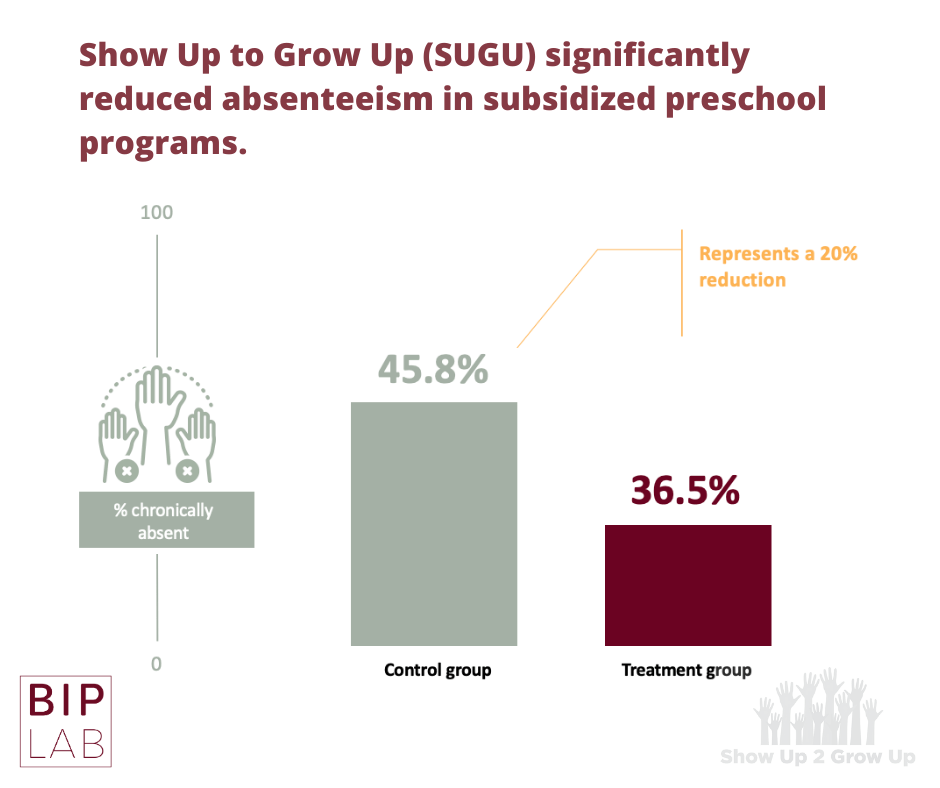
High levels of absenteeism are common in subsidized preschool programs. This concerning trend continues over the course of the child’s education: one-third of chronically absent four-year-olds continue to be chronically absent in kindergarten. Of these students, more than 30 percent are still chronically absent in second grade.
Absenteeism is a problem for preschool children because they miss crucial time to develop kindergarten readiness skills. Behavioral science has shown that individuals often encounter cognitive “roadblocks” that prevent them from engaging in behavior that they themselves want to do. Head Start programs stress the importance of attendance, and low-income children are less often absent from kindergarten than from preschool. This suggests that one or more cognitive “roadblocks” may reduce attendance in the preschool years.
Project Show Up 2 Grow Up (SUGU)
This randomized controlled trial aims to develop a cost-effective and scalable behavioral approach to understanding and reducing absenteeism in Head Start programs. Generously supported by the Joyce Foundation.
For more information please see link below:
Show Up 2 Grow Up Overview
Flash Facts
Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes Published Article
Using Behavioral Insights to Increase Attendance at Subsidized Preschool Programs
USA Today News
Reading at home and school attendance shot up with a cheap, easy solution: Texting
Apolitical Article
A third of Chicago’s poorest kids are “chronically absent” from pre-school
Discover More
News From Our Lab
Join Our Team
Understanding Differences in Parent Investments
